Page 79 - 《广西植物》2020年第2期
P. 79
2 1 6 广 西 植 物 40 卷
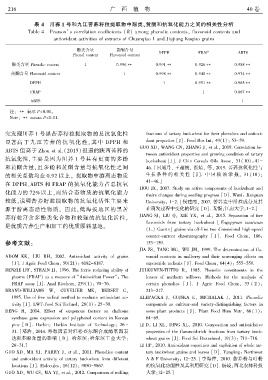
表 4 川荞 1 号和九江苦荞籽粒提取物中酚类、黄酮和抗氧化能力之间的相关性分析
Table 4 Pearson’s correlation coefficients (R) among phenolic contentsꎬ flavonoid contents and
antioxidant activities of extracts of Chuanqiao 1 and Jiujiang Kuqiao grains
酚类含量 黄酮含量
DPPH FRAP ABTS
Phenol content Flavonoid content
酚类含量 Phenolic content 1 0.996∗∗ 0.991∗∗ 0.926∗∗ 0.988∗∗
黄酮含量 Flavonoid content 1 0.998∗∗ 0.940∗∗ 0.974∗∗
DPPH 1 0.951∗∗ 0.965∗∗
FRAP 1 0.867∗∗
ABTS 1
注: ∗∗ 表示 P<0.01ꎮ
Note: ∗∗ means P<0.01.
究发现川荞 1 号黑苦荞籽粒提取物的总抗氧化性 fractions of tartary buckwheat for their phenolics and antioxi ̄
显著高 于 九 江 苦 荞 的 抗 氧 化 性ꎬ 其 中 DPPH 和 dant properties [J]. Food Res Intꎬ 49(1): 53-59.
GUO XDꎬ WANG CNꎬ ZHANG Jꎬ et al.ꎬ 2019. Correlation be ̄
ABTS 值高于 Zhou et al.(2015)报道的陕西苦荞的
tween antioxidant properties and growing condition of tartary
抗氧化性ꎬ主要是因为川荞 1 号具有更高的多酚 buckwheat [J]. J Chin Cereals Oils Assocꎬ 31(10):41 -
和黄酮含量ꎬ且多酚和黄酮含量与抗氧化性之间 46. [国旭丹ꎬ 王超楠ꎬ 张婧ꎬ 等ꎬ 2019. 苦荞抗氧化性与
的相关系数均在 0.92 以上ꎮ 提取物中游离态物质 生长 条 件 的 相 关 性 [ J]. 中 国 粮 油 学 报ꎬ 31 ( 10):
在 DPPH、ABTS 和 FRAP 的抗氧化能力占总抗氧 41-46.]
HOU JXꎬ 2007. Study on active components of buckwheat and
化能力的 72%以上ꎬ而结合态物质的抗氧化能力
theirs changes during seeding progress [D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan
较低ꎬ说明苦荞籽粒提取物的抗氧化活性主要来 University: 1-2. [侯建霞ꎬ 2007. 苦荞麦中活性成分及其
源于游离态活性物质ꎮ 因此ꎬ低海拔地区的黑苦 在萌发过程中变化的研究 [D]. 无锡:江南大学:1-2.]
JIANG SJꎬ LIU Qꎬ XIE YXꎬ et al.ꎬ 2015. Separation of five
荞籽粒富含多酚类化合物和较强的抗氧化活性ꎬ
flavonoids from tartary buckwheat [ Fagopyrum tataricum
是优质苦荞生产和加工的优质原料基地ꎮ
(L.) Gaertn] grains via off ̄line two dimensional high ̄speed
counter ̄current chromatography [ J ]. Food Chemꎬ 186:
参考文献: 153-159.
JIA ZSꎬ TANG MCꎬ WU JMꎬ 1999. The determination of fla ̄
ADOM KKꎬ LIU RHꎬ 2002. Antioxidant activity of grains vonoid contents in mulberry and their scavenging effects on
[J]. J Agric Food Chemꎬ 50(21): 6182-6187. superoxide radicals [J]. Food Chemꎬ 64(4): 555-559.
BENZIE IFFꎬ STRAIN JJꎬ 1996. The ferric reducing ability of JULKUNEN ̄TIITTO Rꎬ 1985. Phenolic constituents in the
plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “Antioxidant Power”: The leaves of northern willows: Methods for the analysis of
FRAP assay [J]. Anal Biochemꎬ 239(1): 70-76. certain phenolics [ J ]. J Agric Food Chemꎬ 33 ( 2 ):
BRAND ̄WILLIAMS Wꎬ CUVELIER MEꎬ BERSET Cꎬ 213-217.
1995. Use of free radical method to evaluate antioxidant ac ̄ KLEPACKA Jꎬ GUJSKA Eꎬ MICHALAK Jꎬ 2011. Phenolic
tivity [J]. LWT ̄Food Sci Technolꎬ 28(1): 25-30. compounds as cultivar ̄and variety ̄distinguishing factors in
DENG Hꎬ 2014. Effect of exogenous factors on chalcone some plant products [J]. Plant Food Hum Nutrꎬ 66(1):
synthase gene expression and polyphenol content in Korean 64-69.
pine [ D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology: 26 - LI Dꎬ LI XLꎬ DING XLꎬ 2010. Composition and antioxidative
31. [邓浩ꎬ 2014. 外源因素对红松查尔酮合成酶基因表 properties of the flavonoid ̄rich fractions from tartary buck ̄
达和多酚含量的影响 [D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学: wheat grains [J]. Food Sci Biotechnolꎬ 19(3): 711-716.
26-31.] LI HPꎬ 2010. Antioxidant capacities and exploition of whole tar ̄
GUO XDꎬ MA YJꎬ PARRY Jꎬ et al.ꎬ 2011. Phenolics content tary buckwheat grains and leaves [D]. Yangling: Northwest
and antioxidant activity of tartary buckwheat from different A & F University: 12-25. [李海萍ꎬ 2010. 苦荞粉与叶粉
locations [J]. Moleculesꎬ 16(12): 9850-9867. 的抗氧化功能性及其利用研究 [D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技
GUO XDꎬ WU CSꎬ MA YJꎬ et al.ꎬ 2012. Comparison of milling 大学:12-25.]