Page 22 - 《广西植物》2023年第7期
P. 22
1 1 9 0 广 西 植 物 43 卷
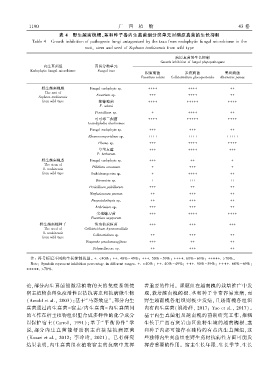
表 4 野生越南槐根、茎和种子各内生真菌组分类单元对病原真菌的生长抑制
Table 4 Growth inhibition of pathogenic fungi antagonized by the taxa from endophytic fungal microbiome in the
rootꎬ stem and seed of Sophora tonkinensis from wild type
病原真菌的生长抑制
Growth inhibition of fungal phytopathogens
内生真菌组 真菌分类单元
Endophytic fungal microbiome Fungal taxa
根腐病菌 炭疽病菌 黑斑病菌
Fusarium solani Colletotriehum gloeosporioides Alternaria panax
野生越南槐根 Fungal endophyte sp. ++++ ++++ ++
The root of
Sophora tonkinensis Fusarium sp. +++ ++++ ++
from wild type 茄镰孢菌 ++++ +++++ ++++
F. solani
Penicillium sp. + ++++ ++
可可球二孢菌 ++++ +++++ ++++
Lasiodiplodia theobromae
Fungal endophyte sp. +++ +++ ++
Rhexocercosporidium sp. ++++ ++++ +++++
Phoma sp. +++ ++++ ++++
草茎点霉 +++ ++++ +++
P. herbarum
野生越南槐茎 Fungal endophyte sp. +++ ++ +
The stem of
S. tonkinensis Pilidium concavum + +++ +
from wild type Dothideomycetes sp. + ++++ ++
Bionectria sp. + +++ ++
Penicillium pulvillorum +++ ++ ++
Neofusicoccum parvum ++ +++ ++
Neopestalotiopsis sp. ++ +++ ++
Arthrinium sp. +++ +++ ++
尖孢镰刀菌 +++ ++++ ++++
Fusarium oxysporum
野生越南槐种子 海水仙炭疽菌 +++ +++ +++
The seed of Colletotrichum hymenocallidis
S. tonkinensis
Colletotrichum sp. ++ +++ ++
from wild type
Diaporthe pseudomangiferae +++ ++ ++
Didymellaceae sp. ++ +++ ++
注: 符号标记不同的生长抑制范围ꎮ +. <40%ꎻ ++. 40% ~ 49%ꎻ +++. 50% ~ 59%ꎻ ++++. 60% ~ 69%ꎻ +++++. >70%ꎮ
Note: Symbols represent inhibition percentage in different ranges. +. <40%ꎻ ++. 40% - 49%ꎻ +++. 50% - 59%ꎻ ++++. 60% - 69%ꎻ
+++++. >70%.
论ꎬ部分内生真菌能激活植物的天然免疫系统使 着重要的作用ꎮ 课题组在越南槐的栽培推广中发
宿主植物获得免疫活性以拮抗害虫和抗病微生物 现ꎬ栽培越南槐的根、茎和种子非常容易发病ꎬ而
(Arnold et al.ꎬ 2003)ꎻ基于“马赛效应”ꎬ部分内生 野生越南槐各组织则极少发病ꎬ且越南槐各组织
真菌通过内生真菌-宿主 / 内生真菌-内生真菌间 内有内生真菌(姚裕群ꎬ 2017ꎻ Yao et al.ꎬ 2017)ꎮ
的互作在宿主植物组织里合成多样性的化学成分 基于内生真菌组及越南槐的前期研究工作ꎬ推测
以保护宿主( Carrollꎬ 1991)ꎻ基于“ 平衡协作” 学 生长于广西石灰岩山区独特生境的越南槐根、茎
说ꎬ部分 内 生 真 菌 能 帮 助 宿 主 直 接 拮 抗 病 原 菌 和种子内部可能存在独特的有益内生真菌组ꎬ这
(Kusari et al.ꎬ 2012ꎻ 李玲玲ꎬ 2021)ꎮ 已有研究 些独特内生真菌组在野生药材抗病性方面可能发
结果表明ꎬ内生真菌组在植物宿主的抗病中发挥 挥着重要的作用ꎮ 宿主生长年限、生长季节、生长